USB cables are ubiquitous in modern computing. They connect a wide range of devices to computers, including keyboards, mice, printers, external hard drives, and more. But with so many different types of USB cables available, it can be difficult to know which one is right for your needs. If you’re unsure about the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 cables, this blog post will explain it to you. Additionally, it will help you decide which one to buy.
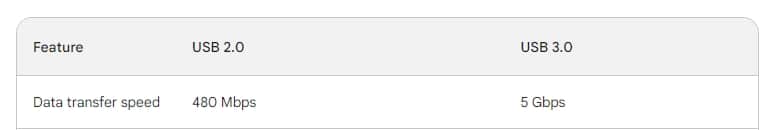
Data Transfer Speed:
USB 2.0: Introduced in 2000, USB 2.0 supports data transfer speeds up to 480 Mbps (Megabits per second). This was a significant improvement over its predecessor, USB 1.1, but it’s relatively slow compared to modern standards. USB 2.0 is adequate for basic tasks like connecting keyboards, mice, and printers, but it can be a bottleneck when dealing with high-bandwidth devices.
USB 3.0: Launched in 2008, USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, offers a dramatic leap in performance, with data transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps (Gigabits per second). This makes it ideal for tasks that involve large amounts of data, such as transferring files between external hard drives or using high-resolution webcams. The increased speed also means faster charging for compatible devices.
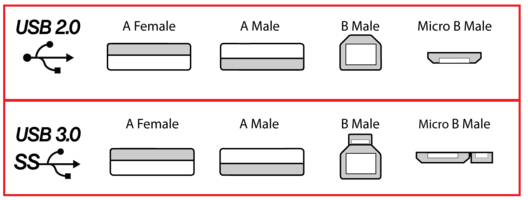
Physical Appearance:
USB 3.0 cables have blue inserts in the connectors, while USB 2.0 cables have white or black inserts. USB 3.0 cables have more wires (9 instead of 4), allowing faster data transfer and improved power management.

Connector Design and Compatibility
USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 Connectors: Physically, USB 3.0 connectors are designed to be backward compatible with USB 2.0 ports. A USB 3.0 cable will fit into a USB 2.0 port, but it will operate at USB 2.0 speeds. Conversely, a USB 2.0 cable cannot take advantage of the higher speeds offered by USB 3.0 ports.
It’s worth noting that USB 3.0 connectors are typically blue on the inside, while USB 2.0 connectors are often black or white. This color coding can help you quickly identify which standard you’re dealing with.
Cable Construction
USB 2.0: Generally, USB 2.0 cables are simpler in terms of construction and cost less. They typically have fewer wires inside, which limits their bandwidth and power delivery.
USB 3.0: These cables have more internal wires (9 compared to USB 2.0’s 4), which enables their higher data transfer rates and increased power delivery. The additional wires help maintain signal integrity and speed. USB 3.0 cables are often thicker and may feel more robust compared to USB 2.0 cables.
Use Cases
USB 2.0: Ideal for everyday peripherals like mice, keyboards, and older printers. If you’re dealing with basic tasks and don’t require high-speed data transfer, USB 2.0 will suffice.
USB 3.0: Best suited for high-performance needs, such as connecting external SSDs, high-definition webcams, and other data-intensive devices. If you’re looking to future-proof your setup or have devices that demand higher data transfer rates, USB 3.0 is the way to go.
Price:
USB 2.0: Generally less expensive and more widely available. Most basic peripherals and older devices use USB 2.0, which keeps costs down.
USB 3.0: Slightly more expensive due to the advanced technology and additional components. However, as USB 3.0 has become the standard for new devices, the price difference is narrowing, and USB 3.0 cables are increasingly affordable.

Compatibility:
USB 3.0 cables and ports work with USB 2.0 devices, so you can use them together. However, the performance will be limited by the lower standard. For example, if you use a USB 3.0 cable with a USB 2.0 port, you will only get the speed and power of USB 2.0. Similarly, if you use a USB 2.0 cable with a USB 3.0 port, you will not enjoy the benefits of USB 3.0 cable

When to use USB 2.0 cables
USB 2.0 cables are a good choice for basic tasks such as connecting a keyboard, mouse, or printer to a computer. They’re good for connecting devices with low bandwidth needs, like an external DVD drive or a flash drive.
When to use USB 3.0 cables
USB 3.0 cables are a good choice for demanding tasks such as transferring large files or connecting external hard drives. They’re also a good choice for connecting devices that require a lot of bandwidth, such as a high-definition webcam or a gaming controller.
Which type of USB cable should you buy?
If you’re not sure which type of USB cable you need, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and buy a USB 3.0 cable. USB 3.0 cables are backwards compatible with USB 2.0 devices, so you can still use them with older devices if needed.
In conclusion, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 cables have different advantages and disadvantages, and you should consider them before you buy. USB 3.0 cables are faster, more efficient, and more future-proof, but they are also more expensive and less common. USB 2.0 cables are slower, less efficient, and more outdated, but they are also cheaper and more widely supported. Ultimately, the choice is yours, but we hope this blog post has helped you make an informed decision.
Related Products
Wandkey is a MFI certified cable and charger manufacturer, supports OEM/ODM service, printing logo, customized packaging, color, length, mould etc. Welcome to contact us get the quotation and samples for the test.
Any questions feel free to contact us, we would be happy to solve your issues
Related Topics
2022 Latest MFi Authorized Manufacturers list
Differences of Lightning Connector
How to check MFI Certification
How to get MFI Certification for Your Brand?
Why does the MFI Certified Lightning Cable so expensive?
MFI Product Packaging Requirement?
Disassemble MFI Lightning Cable
iPhone 14 Pro may use USB C Charging Port
How do we guarantee the quality?
How to identify counterfeit or uncertified Lightning connector accessories
How to Choose Fast Charging Cable for Your Phone
How do I choose a USB-C cable?
Differences between USB 3.0 3.1 and 3.2
Test on USB C to USB C 3.1 Cable














